What Are Cloud Servers?
Cloud servers are virtual machines that operate within a cloud computing environment rather than on a single physical machine. They are created using virtualization technology, which divides the resources of many physical servers into multiple independent virtual environments.
Unlike traditional servers that depend on a single device, cloud servers draw power from a pool of interconnected hardware. If one machine fails, another automatically takes over. This is what makes cloud systems resilient, flexible, and highly available.
The “cloud” itself is not a single place — it is a massive network of data centers spread across regions and countries. These data centers contain thousands of physical servers connected through high-speed networks and controlled by advanced software layers.
Where Cloud Servers Get Their Power
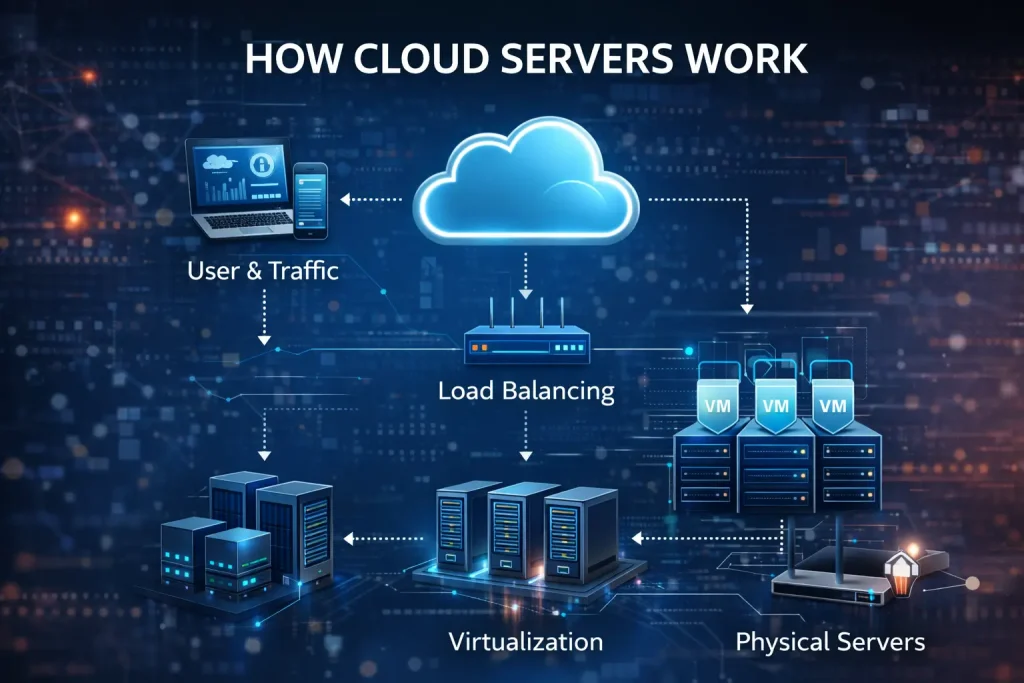
The real strength of cloud servers comes from three technical layers:
- Physical Data Centers
These facilities contain racks of high-performance servers, networking equipment, power supplies, and cooling systems. They are designed to run 24/7 with backup power and disaster recovery systems. - Virtualization Technology
Hypervisors divide physical machines into multiple virtual servers. Each cloud server runs its own operating system and applications, fully isolated from others. - Distributed Resource Pools
Instead of relying on one computer, cloud servers use shared pools of CPU, memory, storage, and bandwidth. These resources can be increased or decreased instantly.
How Cloud Servers Work in Practice
When a business creates a cloud server, it is not assigned to one physical machine. Instead, it becomes part of a cluster. Load balancers distribute incoming requests to the least busy servers. If one node fails, another takes over automatically.
Data is often replicated across multiple locations. This means even if a data center goes offline, the service continues from another region.
This design eliminates single points of failure, which is one of the biggest weaknesses of traditional hosting.
Why Shared Hosting Is Being Replaced
Shared hosting places hundreds of websites on one physical server. All users compete for the same CPU, memory, and bandwidth. When one site experiences high traffic, all others slow down.
Cloud servers, by contrast, isolate each environment and allow instant scaling. Businesses can increase resources during peak demand and reduce them when traffic is low.
Shared hosting is cheap, but limited. Cloud servers cost more, but provide stability, performance, and control that shared environments cannot.
Performance and Scalability
One of the biggest advantages of cloud servers is elastic scaling. Businesses can add or remove resources within minutes, without shutting down their systems.
This makes cloud servers ideal for:
- Online stores during sales events
- Media platforms during viral traffic
- Financial services during peak hours
Traditional hosting cannot adapt at this speed.
Security Advantages of Cloud Servers
Cloud infrastructure is built with security at its core. Providers implement:
- Firewalls and network segmentation
- Encrypted data storage
- Identity and access controls
- Real-time monitoring and alerts
Because data is distributed and backed up, cloud servers are also more resistant to ransomware and hardware failures.
Main Business Uses
Cloud servers are widely used for:
- E-commerce platforms
- SaaS applications
- Online banking systems
- Streaming services
- Corporate websites and APIs
They support remote teams, automation, and global services.
Top Countries Producing Cloud Infrastructure
- United States
- Germany
- Ireland
- Singapore
- Japan
These countries host major data centers and cloud hubs.
Top Countries Consuming Cloud Services
- United States
- United Kingdom
- India
- Canada
- Australia
Demand is driven by digital transformation and e-commerce growth.
Cost Comparison
Shared hosting is the cheapest option but has strict limits.
Cloud servers are more expensive but charge based on usage, allowing businesses to pay only for what they consume.
⚠️ Warning
Misconfigured cloud servers can expose sensitive data. Security settings must always be reviewed and updated.
The Future of Cloud Infrastructure
Artificial intelligence, edge computing, and automation will make cloud servers faster, smarter, and more adaptive. Businesses that adopt early will gain a strong competitive advantage.
(FAQ)
- Are cloud servers more secure than traditional servers?
Cloud servers use multiple security layers such as encryption, firewalls, access control, and monitoring, which often make them more secure than single physical servers when properly configured. - Can a cloud server replace shared hosting completely?
Yes. For growing websites and businesses, cloud servers offer better performance, scalability, and reliability than shared hosting, making them a long-term replacement. - Do cloud servers go down if one data center fails?
No. Cloud systems are designed with redundancy. If one data center fails, traffic is automatically routed to another location. - Are cloud servers expensive for small businesses?
Cloud servers use a pay-as-you-go model. Small businesses can start with low resources and scale only when needed, which makes them cost-efficient. - What is the main difference between a cloud server and a VPS?
A VPS runs on one physical server, while a cloud server runs on a cluster of servers, allowing higher availability and scalability.
⚠️ Important Notice
Although cloud servers provide high availability and scalability, they still require proper configuration and regular maintenance. Weak passwords, open ports, and outdated software can turn even the most advanced cloud system into a serious security risk. Always apply updates, restrict access, and monitor activity to protect your data.
Sources
Wikipedia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cloud_computing
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cloud_server
Cloudflare
https://www.cloudflare.com/learning/cloud/what-is-a-cloud-server/
https://www.cloudflare.com/learning/cloud/what-is-cloud-computing/
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
https://aws.amazon.com/what-is/cloud-server/
https://aws.amazon.com/what-is/cloud-computing/
Google Cloud
https://cloud.google.com/learn/what-is-cloud-computing
https://cloud.google.com/learn/what-is-cloud-server
Microsoft Azure
https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/resources/cloud-computing-dictionary/what-is-cloud-computing/
https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/resources/cloud-computing-dictionary/what-is-a-cloud-server/




